Discover the power of light.
Discover the power of light.
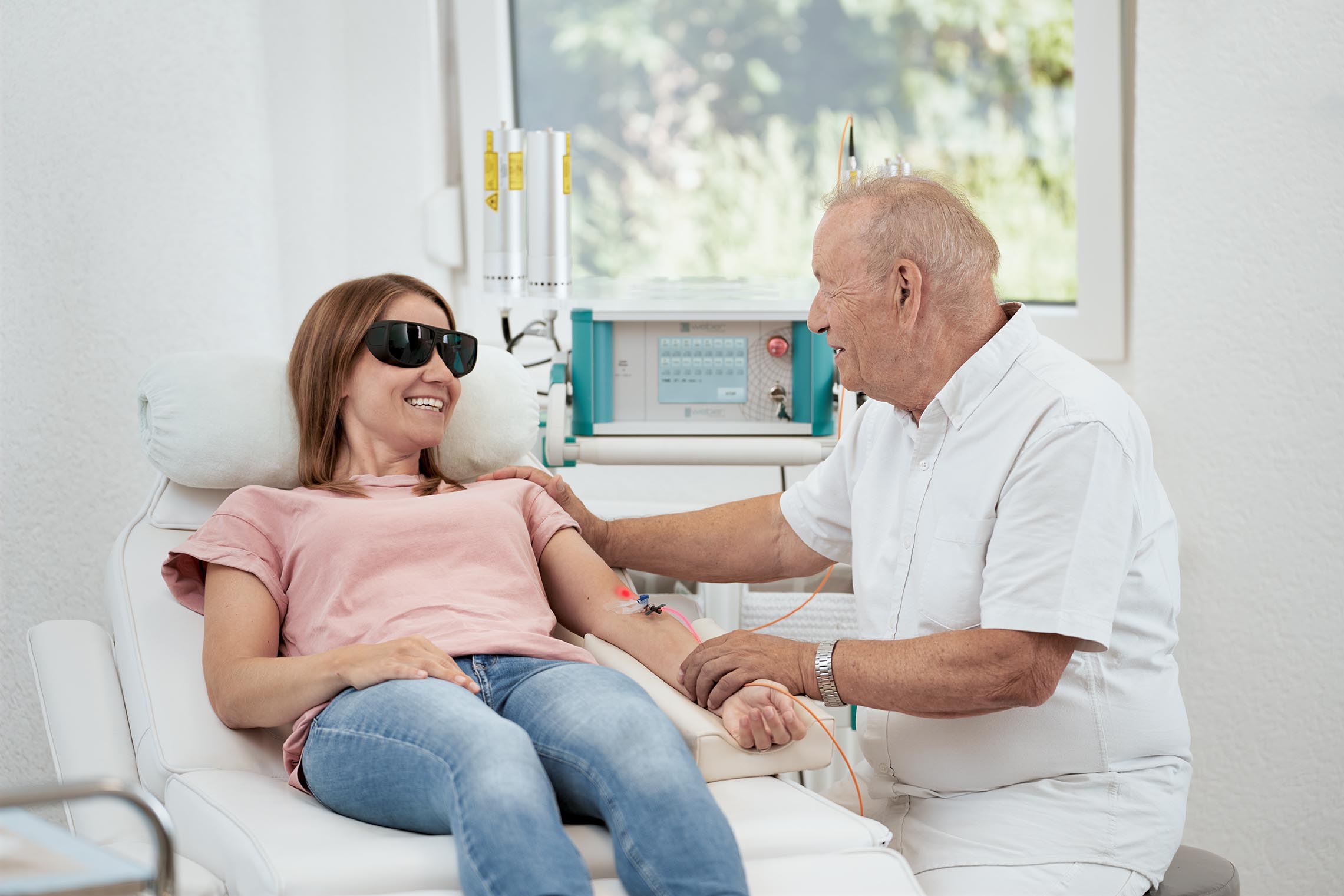
Low-Level Laser Therapy for your clinic
Revolutionizing medical laser technology with the Weberneedle® Endolaser System.
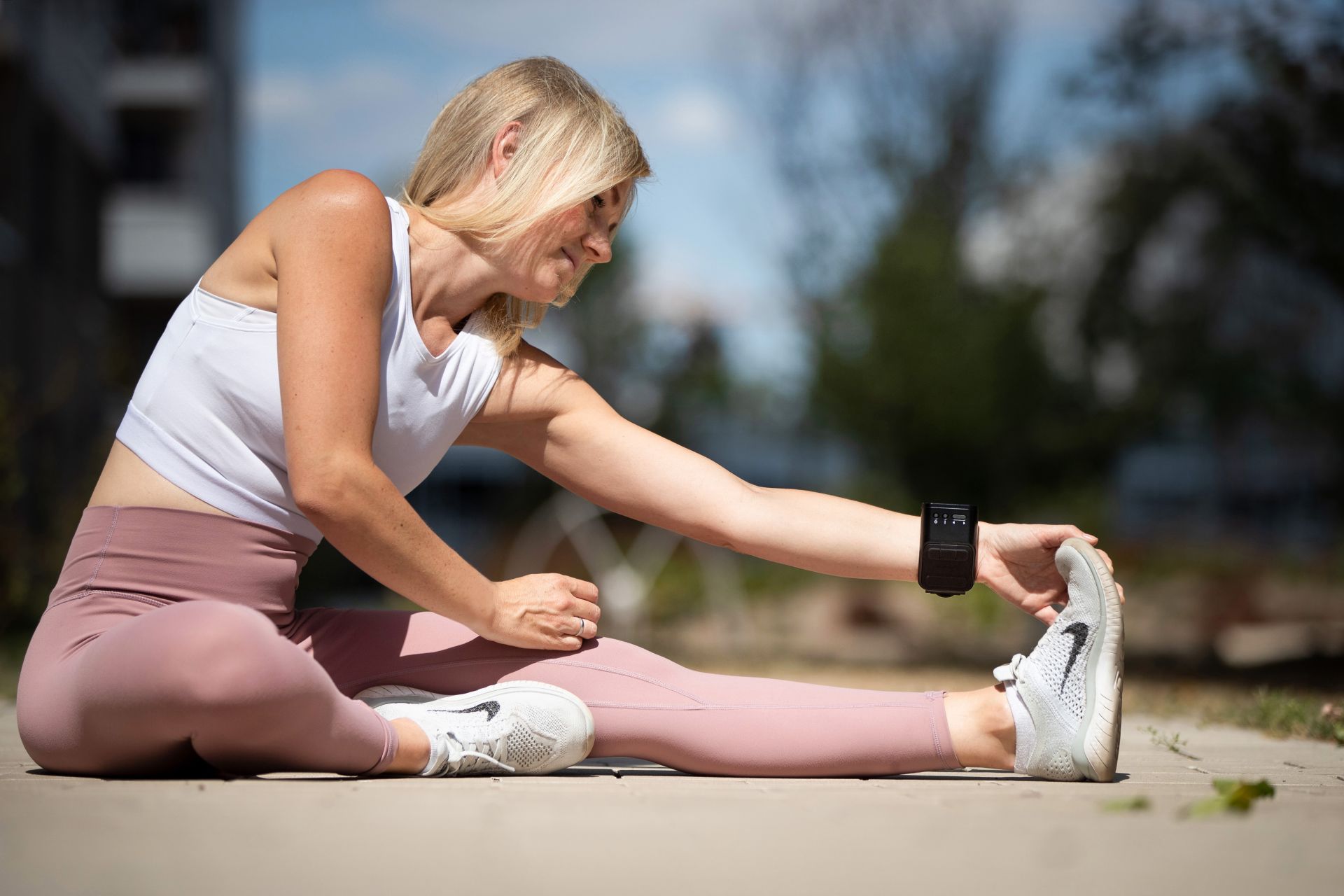

Experience the therapeutic effectiveness of light
Innovative solutions for your daily routine.

Low-Level Laser Therapy for your clinic
Revolutionizing medical laser technology with the Weberneedle® Endolaser System.

Experience the therapeutic effectiveness of light
Innovative solutions for your daily routine.
For Clinics
Weber Medical GmbH
Tel: +49 5273 367 780
Fax: +49 5273 367 7819
info@webermedical.com
For Home Use
Weber Medical Systems GmbH
Tel: +49 5273 389 4506
info@wmedicalsystems.com
Shop: wmedicalsystems.com
© 2025 All Rights Reserved.
